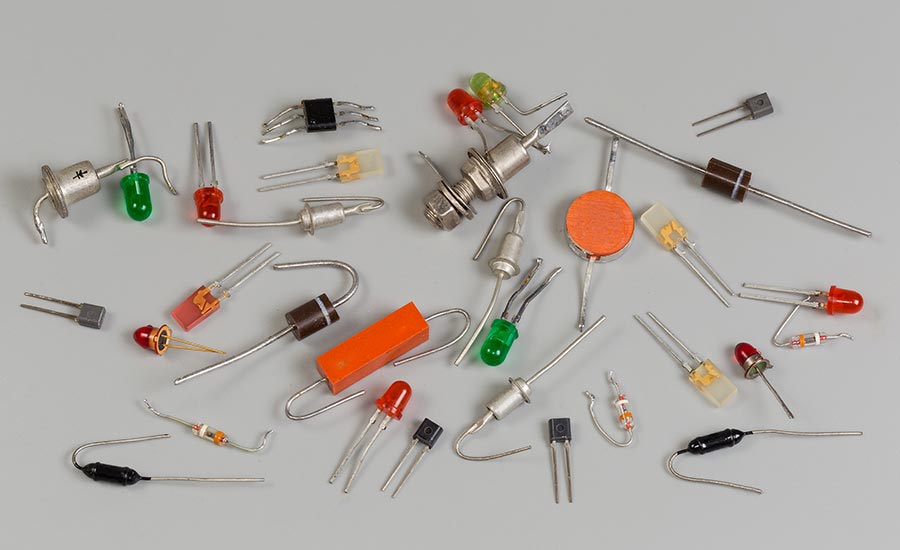

In a tech-driven world that’s always pushing boundaries, diodes remain at the core of electronic improvements and advancements as diode applications continue to expand.
The diodes global market had a rough valuation of $7.36 billion in 2023, and the future is looking bright for this industry as the diodes market is expected to grow to nearly $9.54 billion by 2030.
Today, we’re going to take a closer look at different types of diodes, explain their roles in electronic systems and briefly go through popular industries where they are used the most.
What Is a Diode?
A diode is an electronic component and a semiconductor device that basically acts as a one-way switch for electrical current in a circuit.
This ability to move in one direction is also known as unidirectional conductivity and is key to managing electrical signals and protecting circuits from potential damage mostly caused by reverse currents.
When explaining what a diode is, it’s also important to understand that a diode has a fundamental component called P-N junction. This is where two types of semiconductor materials, called P-type (positive) and N-type (negative), meet.
How Does a Diode Work?
We already explained that a diode controls the flow of electrical current using two types of semiconductor materials, but how exactly does it work?
- Forward bias: When the positive voltage is applied to the P-side and negative voltage to the N-side, the P-N junction reduces its internal resistance, which makes the current flow.
- Reverse bias: When the polarity is reversed in the reverse bias, the positive voltage needs to be applied to the N-side and negative to the P-side. This creates two end results as it increases the resistance of the junction, while also blocking current flow.
- Breakdown voltage: While diodes are designed to block reverse currents, exceeding a specific threshold voltage can cause the diode to conduct in reverse, a feature intentionally used in Zener diodes for voltage regulation.
Different Types of Diodes and Their Functions
Diodes come in various types, and each type has a specific purpose in the electronic circuit.
The most common types of diodes include:
1. Rectifier Diodes
Typically created for alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC), rectifier diodes facilitate an essential process for powering electronic devices.
They’re mostly used in power supplies for converting household AC power into the DC power required by electronics.
Take a laptop charger, for example. Inside the charger, rectifier diodes convert wall socket electricity into stable DC power to charge your battery safely.
2. Zener Diodes
These diodes are created to regulate voltage and protect circuits using reverse bias mode.
The reason why they are ideal for voltage regulation is because they allow current to flow in reverse once a specific voltage is reached.
For example, mobile phones have Zener diodes because they provide microprocessors in the phone with stable voltage at all times.
3. Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
LEDs are diodes that emit light when an electric current passes through them, making them energy-efficient and versatile light sources.
LEDs use electroluminescence to convert electrical energy directly into light, with minimum heat generation.
You’ve probably seen LED bulbs that can either change colors based on a preset pattern or sync dynamically to a pattern of a song, making any room feel like a party.
4. Schottky Diodes
Known for their low forward voltage drop and fast switching capabilities, Schottky diodes are the best choice for high speed and high-efficiency applications.
These diodes have a metal-semiconductor junction instead of a P-N junction, allowing them to operate at higher speeds with minimal energy loss.
For example, Schottky diodes in computer processors enable quick data transfer by improving the speed of logic circuits.
5. Photodiodes
They are light-sensitive diodes that generate or control electrical current when exposed to light.
Photodiodes convert light into electrical signals, making them ideal for sensing applications. They are highly sensitive and respond quickly to changes in light intensity.
They’re also critical in fiber-optic communication, where they detect light signals transmitted over long distances, ensuring fast and reliable internet connectivity.
Applications of Diodes in Electronics
The versatile function of diodes is rapidly being implemented in many new applications.
Applications of diodes in electronics include:
1. Diodes in Power Supplies
Diodes are required for converting and stabilizing electrical power. Rectifier diodes for example, are used in power supplies to convert AC to DC, ensuring electronic devices operate reliably.
Example: Every time you charge your smartphone or your laptop, diodes in the charger convert household AC electricity into DC power.
2. Signal Processing Applications
Diodes are used for controlling, filtering, and amplifying electrical signals in signal processing applications. Their ability to regulate current flow and rectify signals makes them a core electronic component in audio and communication systems.
Example: In radios, diodes demodulate AM or FM signals, transforming them into audible sound. Comparably, in audio systems, diodes prevent interference and stabilize signals, providing clear sound quality for your favorite songs or podcasts.
3. Diodes in Lighting and Display Technologies
LEDs have revolutionized lighting and displays, offering energy-efficient and durable solutions for various applications. These light-emitting diodes convert electrical energy into light with minimal heat generation.
Example: LED TVs, smartphones, and smartwatches — they all rely on LEDs for vibrant, high-resolution displays that we experience on a daily basis.
4. Telecommunications and Automotive Systems Diode Usage
In telecommunications and automotive industries, diodes are mostly used to boost performance, provide reliability, and manage power effectively.
- Diodes in telecommunications: The photodiodes in fiber-optic networks are mostly used in telecommunications because they are able to detect light signals, providing high-speed internet and data transmission. The most common type of diode in this case is the Schottky diode, because it supports quick switching for signal amplification, improving the process of communication systems.
- Diodes in automotive systems: Zener diodes act as guardians of automotive control systems, as they stabilize voltage to protect delicate electronics from power spikes. They’re also used in sleek designs of certain cars, where LEDs illuminate dashboards and taillights while consuming less power, such as Tesla’s brake lights or their monitors.

Why Choose High-Quality Diodes From AGS Devices?
At AGS Devices, we fully understand the important role diodes play in the performance and reliability of electronic systems.
Our constant commitment to quality, precision, and customer satisfaction sets us apart as a trusted partner for sourcing electronic components such as various types of diodes.
Besides diodes, we also distribute electronic components such as:
- Power Supply Distributors
- Semiconductors for Sale
- Circuit Protection
- Interconnects
- Passive Components Electronics
- Electronic Testing Equipment
- Electromechanical Devices
Whether you need LEDs, photodetectors or optical fibers for networking, our team will provide you with the best quality electronic components available on the market.
