Electronic Components: Key Points
- Electronic components are divided into active components (like transistors and ICs) that amplify or switch signals, and passive components (like capacitors and resistors) that store or regulate energy
- They form the building blocks of every electronic circuit, from consumer gadgets to industrial control systems
- Both essential in modern devices, digital electronics use discrete signals (1s and 0s) while analog electronics process continuous signals
- A standard electronic components list includes parts such as microprocessors, diodes, transformers, and potentiometers
- Understanding electronic symbols and component behavior helps engineers troubleshoot, repair, and design more efficiently
The latest statistics show that the global electronic components market was valued at USD 186.38 billion.
These components, varying from simple resistors to complex integrated circuits, are integral in devices like smartphones, computers, and sophisticated industrial machinery.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
- The difference between active and passive electronic components
- Real-world examples of how components like resistors, capacitors, and microcontrollers power modern tech
- The role of analog and digital electronics in today’s devices
- How to identify common electronics components by function and application
- Why sourcing high-quality components is critical for long-term reliability
Types of Electronic Components
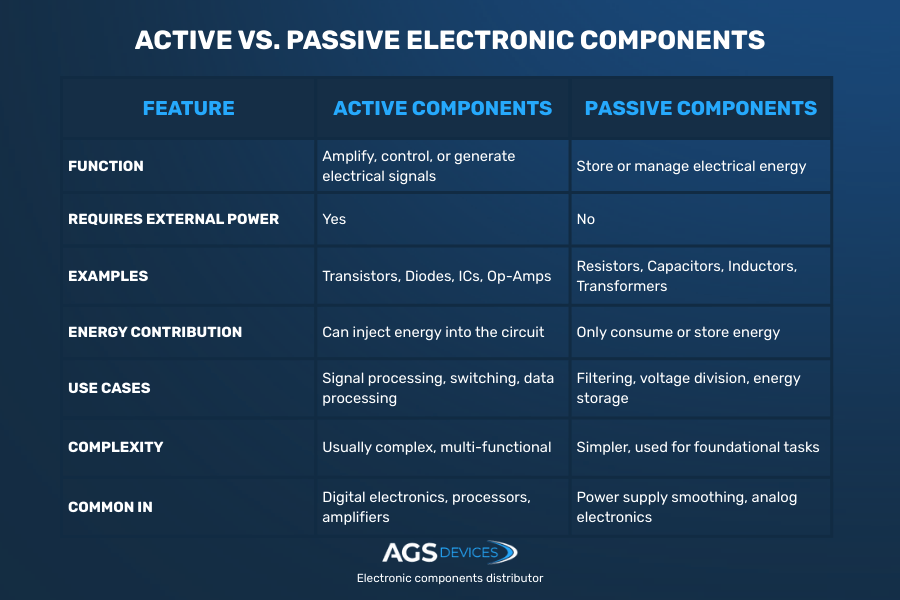
Electronic components can be categorized into two main types: active components and passive components.
Active Components
Active components can introduce energy into a circuit and can amplify or process electrical signals. They are key to control and contain electrical power and information in a circuit.
Active components include:
- Transistors
- Diodes
- Integrated Circuits (ICs)
- Microprocessors
- Microcontrollers
- Operational Amplifiers (Op-Amps)
Passive Components
Passive electronic components cannot introduce energy into the circuit. They only consume or store energy.
Passive components include:
- Resistors
- Capacitors
- Inductors
- Transformers
- Potentiometers
Functions and B2B Usage of Active and Passive Electronic Components
Each electronic component, whether active or passive, plays a pivotal role in the overall functioning and stability of a circuit.
We’re going to explain the difference between active and passive components and elaborate on where they’re used the most.
Active Components: Function and Usage
Active components enable functions such as amplification and signal processing.
The most common active components include:
- Transistors: Transistors are the most essential active components in electronic circuits. They function primarily as switches. They can turn a signal on or off and amplify weak signals. They are widely used in circuit boards for computers and industrial machinery and are integral in controlling operations and processing signals. In telecommunications, they are key for amplifying signals in transceivers and network equipment.
- Diodes: Diodes allow current to flow in one direction, which is essential for rectification and signal modulation. They are used in power supply units for converting AC to DC, in communication devices for signal demodulation, and in industrial automation for controlling current flow.
- Integrated Circuits (ICs): ICs can perform a vast array of functions, from simple timing tasks in a quartz watch to complex processing in a computer’s central processing unit. ICs are the brains behind most modern electronics, including computers, smartphones, and industrial control systems.
- Microprocessors: Microprocessors handle digital data by executing instructions from the device’s memory. Office equipment, advanced manufacturing systems, and the operational control of various machinery and vehicles commonly use microprocessors.
- Microcontrollers: These are specialized ICs designed to control specific operations in an electronic device. They are commonly used in embedded systems for controlling machinery, in automotive electronics for managing functions like engine control, and in various IoT (Internet of Things) devices for smart industrial applications.
- Operational Amplifiers (Op-Amps): Used in signal processing, Op-Amps can amplify a wide range of signal types. They’re used in industrial measurement and control instruments, in audio processing equipment, and in medical devices for signal amplification and conditioning.
Passive Components: Function and Usage
Passive components control, stabilize, and facilitate the flow of electricity in a circuit.
The most common passive components include:
- Resistors: All resistor types resist the flow of electricity, helping to manage current and voltage levels within a circuit. They are used in manufacturing control circuits, power supply systems, and telecommunications equipment for impedance matching and signal conditioning.
- Capacitors: Capacitors store and release electrical energy, playing a key role in filtering out noise, stabilizing voltage, and storing energy temporarily. Many types of capacitors are crucial in power electronics, energy storage systems, and application filtering in telecommunications. They also play a role in smoothing out power fluctuations in industrial machinery.
- Inductors: Inductors store energy in a magnetic field. Many types of widely used in power supplies for filtering noise and in RF (radio frequency) applications for signal processing. Inductors are also integral in the automotive industry for electronic control systems.
- Transformers: These components transfer electrical energy between two circuits without direct electrical connection. Various types of transformers are key in power distribution networks, in medical imaging equipment, and in audio systems for impedance matching.
- Potentiometers: As variable resistors, these devices enable the manual adjustment of resistance in a circuit. They are commonly used in industrial control panels for setting levels or calibration, in professional audio equipment for volume control, and in automotive dashboards for adjusting various settings.
How Electronic Components Work Together
The interaction of electronic components in a circuit is a teamwork effort, where each element plays a specific role and their collective operation creates a functioning system.
Basic Circuitry
In basic circuitry, the primary goal is to control the flow of electric current in a desired way to perform a specific function. A combination of various electronic components, each contributing its unique property, helps achieve this control.
- The combination of electronic components include:
- Resistors control the flow of current, ensuring that other components receive the appropriate current and voltage.
- Capacitors store and release energy, acting as temporary energy buffers and helping to smooth out power supply fluctuations.
- Inductors, much like capacitors, store energy, but in a magnetic field. This is particularly useful in filtering and tuning applications.
- Transistors act as amplifiers or switches. As amplifiers, they boost the strength of an incoming signal. As switches, they control the flow of current in response to an input signal.
Examples of Simple Circuits
- LED Flasher Circuit: This basic circuit uses a transistor to periodically turn on and off an LED. The timing of the flashing is controlled by a resistor-capacitor (RC) network. When the capacitor charges to a certain voltage, the transistor turns on, lighting the LED. As the capacitor discharges, the transistor turns off and the LED goes out. This cycle repeats, creating a flashing effect.
- Simple Radio Receiver: This circuit uses a diode to demodulate (extract) audio signals from radio waves. The diode rectifies the received radio frequency signal, allowing only half of the wave (either the positive or negative part) to pass through. An inductor and a capacitor form a tank circuit that selects the frequency of the desired radio station, and a headphone or speaker connected to the circuit enables listening to the audio.
- Voltage Divider: This is a basic circuit consisting of two resistors connected in series. By choosing resistors with suitable values, this circuit can divide the input voltage to a lower output voltage. This is a fundamental concept in designing electronic circuits where specific voltage levels are required.
In these examples, components like resistors, capacitors, transistors, and diodes work with each other to achieve specific functions — from blinking an LED to receiving radio signals.
The Importance of Electronic Components
Electronic components are the building blocks of modern technology, playing crucial roles in various sectors. They are integral to various devices, from everyday consumer electronics to complex industrial machinery.
Consumer Electronics
In the realm of consumer electronics, electronic components are indispensable. They are the heart and soul of various devices that have become integral to daily life:
- Smartphones: Smartphones are one of the most used electronic devices today. Components like microprocessors, memory chips, and sensors work together to provide processing power, storage, connectivity, and interactive capabilities for smartphones.
- Televisions and monitors: LCDs, LEDs, capacitors, and ICs are key in displaying images and powering the advanced features of modern TVs and computer monitors.
- Home appliances: From microwaves to refrigerators, electronic components control functionalities, ensure energy efficiency, and provide connectivity and intelligent features in smart appliances.
- Audio and video equipment: Amplifiers, resistors, capacitors, and transistors are fundamental in audio and video devices, influencing the quality and characteristics of sound and visuals.

Industrial Applications
In the industrial sector, electronic components are the backbone of various systems and machinery, enabling automation, control, and efficiency.
Electronic components are used mostly in industries such as:
- Aerospace industry: In the aerospace industry, aerospace electronic components are important for both navigation and communication systems in aircraft and spacecraft. Microcontrollers, sensors, and communication modules are integral for flight control systems, monitoring engines, fuel systems, and environmental controls.
- Automotive industry: The automotive sector is increasingly relying on automotive electronic supply due to the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Components like sensors, microcontrollers, and power electronics are vital for engine management systems, infotainment systems, and safety features like airbags and ABS.
- Consumer electronics industry: This industry covers a wide range of everyday devices such as smartphones, laptops, home appliances, and entertainment systems. Components like ICs, transistors, diodes, and capacitors are fundamental in these products.
- Industrial sector: Electronic components in the industrial sector are crucial for automation, control systems, and machinery operation. Sensors, actuators, PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), and industrial PCs are the backbone of modern manufacturing, process control, and robotics.
- Medical industry: Medical electronic components are used in many diagnostic, monitoring, and therapeutic devices. This includes everything from portable blood glucose monitors to complex imaging machines like MRI and CT scanners.
- Military industry: Military applications require electronic components that can operate reliably in the most demanding conditions, including extreme temperatures, vibrations, and electromagnetic interference. Components are used in communication systems, surveillance equipment, navigation, and weaponry.
- Renewables industry: In the renewable energy sector, particularly in solar and wind energy systems, electronic components are essential for energy conversion, storage, and management. Inverters, controllers, and battery management systems use semiconductors, capacitors, and resistors to efficiently convert and distribute renewable energy.
- Telecommunications: This industry heavily relies on various telecom electronic components for data transmission and communication. Components like amplifiers, modulators, antennas, and switches are used in a broad spectrum of infrastructure, ranging from cellular towers to satellites.
Electrical Components: Key Takeaways
Electronic components work in harmony as each one has a specific role that impacts the performance and functionality of the entire system.
Component identification and sourcing matter, as low-quality or mismatched parts can cause system failure or performance issues.
Active and passive components serve different functions but are equally important in both simple and complex circuits.
Industries ranging from telecommunications to renewables rely on precise component selection for safety, efficiency, and innovation.
AGS Devices provides not just the parts, but the expert support and supply chain solutions engineers and manufacturers rely on to build better systems — take a look below.
AGS Devices: A Trusted Distributor of Electronic Components
AGS Devices is a leading distributor of electronic components, and our goal is to boost the efficiency and reliability of your supply chain in this specialized and dynamic field.
We also distribute electronic components such as:
- Power Supply Distributors
- Semiconductors for Sale
- Optoelectronics
- Circuit Protection
- Interconnects
- Passive Components Electronics
- Electronic Testing Equipment
- Electromechanical Devices
Besides distribution and testing of electronic components, we also offer services such as:
- Sourcing and Procurement
- BOM Management
- Shortage & Obsolescence Solutions
- Excess Material Acquisition
Our knowledgeable team uses the latest technology and industry insights to provide top-tier testing solutions at competitive prices.
FAQs About Electronic Components
Still have questions about electronic components?
Here is some additional information about electronic components you might find useful:
What are basic electronics and how do they work?
Basic electronics refers to the foundational knowledge and components that make modern technology function, from home appliances to industrial control systems.
Understanding basic electronics is essential for designing, repairing, or sourcing reliable electronics components.
Most electronic circuits consist of electrical parts like resistors, capacitors, and transistors, all working together to control electrical energy flow.
What are electronic components?
Electronic components are devices or elements with specific electrical properties that are used to assemble electronic circuits and systems. These components are the fundamental building blocks of modern electronics and play a crucial role in controlling and manipulating electrical signals.
What are electrical symbols?
Electrical symbols are graphical representations used in circuit diagrams and electrical schematics to depict various electrical and electronic components and their functions. These symbols provide a standardized way to communicate the design and layout of electrical circuits.
What are basic circuit components?
Basic circuit components are the fundamental elements used to construct electrical and electronic circuits.
Basic circuit components include:
- Resistors
- Capacitors
- Inductors
- Diodes
- Transistors
- Integrated Circuits
- Batteries
- Switches
- Fuses
- Light Emitting Diodes (LED)
- Transformers
- Potentiometers
