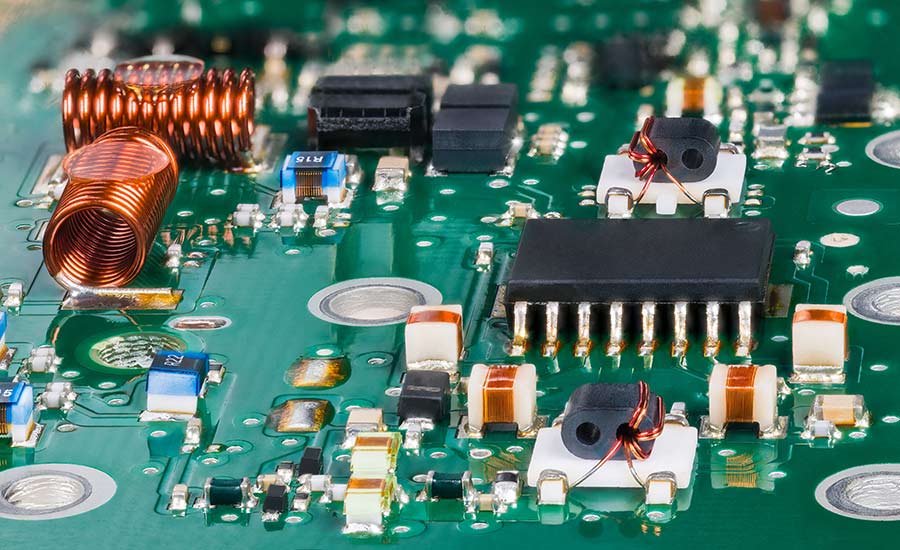
Circuit components serve as the fundamental building blocks of modern electronics, enabling the functionality and innovation of countless devices we use on a daily basis.
From the resistors and capacitors that regulate power flow to the integrated circuits that act as the brains of complex systems, these components are irreplaceable.
The global electronic components market reflects this importance, with projections estimating it will reach approximately $233 billion by 2025, driven by advancements in consumer electronics, automotive technology, and industrial automation.
In this blog, we’re going to cover various types of circuits, essential circuit components and explain different applications in various industries.
What Is an Electric Circuit?
An electric circuit is the foundational system that enables the flow of electrical energy, powering everything from small electronic gadgets to massive industrial machinery.
At its core, an electric circuit consists of a network of components that guide the flow of electrical current to perform a specific function, such as lighting a bulb, running a motor, or transmitting data.
What Are Circuit Components?
Circuit components are the fundamental building blocks of any electrical circuit. These components work together to control the flow of electrical energy, enabling circuits to perform specific functions.
Whether it’s a simple flashlight or a complex industrial automation system, circuit components play a critical role in making sure that electrical systems operate efficiently and reliably.
Circuit components can be broadly categorized into three main types:
- Passive components
- Active components
- Electromechanical components
Types of Electrical Circuits
Each type of electrical circuit offers unique characteristics and is made for different applications, making them foundational to modern electronics.
Most common types of electrical circuits include:
1. Series Circuits
In a series circuit, components are connected end-to-end in a single pathway, meaning the same current flows through all components.
Examples:
- String lights: Holiday string lights are often wired in series, where the removal of one bulb disrupts the entire circuit.
- Safety devices: Certain alarm systems use series circuits to ensure the failure of one component (e.g., a sensor) triggers an alert.
While series circuits are easy to design and maintain, their reliance on a single pathway can be a disadvantage if continuity is interrupted.
2. Parallel Circuits
In parallel circuits, components are connected across multiple paths, allowing current to flow through each pathway independently.
Examples:
Home electrical systems: Residential lighting and outlets use parallel circuits so devices can operate independently.
Automotive systems: Car headlights are wired in parallel so they can function independently even if one fails.
Parallel circuits are ideal for scenarios where consistent operation is critical, as they maintain functionality even when individual components fail.
Mixed Circuits
Mixed circuits, also known as combination circuits, integrate elements of both series and parallel configurations.
Examples:
- Industrial machinery: Manufacturing equipment often uses mixed circuits to separate control systems (series) from operational systems (parallel).
- Consumer electronics: Devices like televisions and computers use mixed circuits to optimize power distribution and performance.
Essential Electric Circuit Components
Every electric circuit relies on a variety of components, each with a specific role in regulating, generating, or transmitting electrical energy.
Essential electric circuit components include:
1. Passive Components
Passive components are the stabilizers of an electric circuit and manage energy without requiring an external power source, so the circuit can operate efficiently and reliably.
For example, resistors control current flow and are vital in devices like LED lighting systems.
Capacitors are used to store and release energy, often employed to filter noise in power supplies.
Meanwhile, inductors manage magnetic fields, making them indispensable in applications like wireless charging systems and RF circuits.
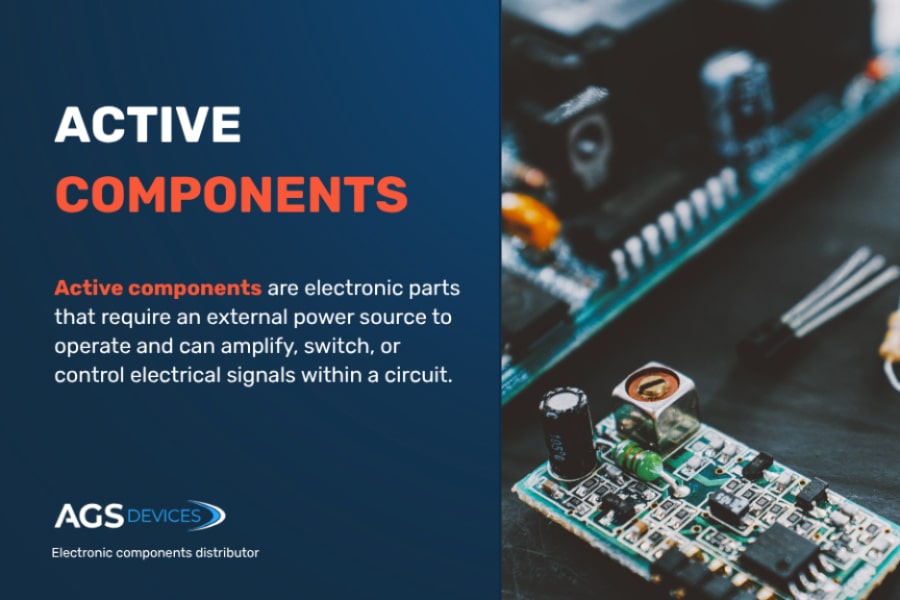
2. Active Components
Active components bring circuits to life by amplifying signals or generating power. These components rely on an external energy source and play a central role in powering modern technology.
Take transistors, for example, which amplify and switch electronic signals in microprocessors, used in creating the main systems of smartphones.
Diodes direct the flow of current and safeguard circuits from power surges, while integrated circuits (ICs) combine multiple functions, making compact designs possible for advanced systems like robotics and IoT devices.
3. Interconnect Components
Interconnect components form the physical and electrical pathways that link a circuit, providing functional operation and communication between parts.
Connectors, for example, are used to join components securely, making them essential in computer systems and industrial equipment.
Switches control the flow of current in devices like power tools and light fixtures, while wires and cables transmit signals and power, forming the backbone of any circuit.
Applications of Circuit Components in Modern Electronics
Circuit components are essential in powering innovations across industries, providing reliability, efficiency, and precision in a wide range of applications.
Here’s how they are utilized in key industries:
1. Consumer Electronics
Circuit components are the driving force behind the functionality and innovation of the devices we use daily.
The most common consumer electronics components are:
- Resistors and capacitors: Regulate power flow in devices like smartphones, laptops, and gaming consoles, providing smooth and safe operation.
- Integrated circuits (ICs): Serve as the brains of smart TVs, wearable devices, and home automation systems, enabling advanced functionality in compact designs.
- Transistors: Amplify signals in audio equipment, providing enhanced sound quality for headphones, speakers, and home theater systems.
2. Automotive Electronics
In the automotive sector, circuit components enable advanced technologies for safety, performance, and energy efficiency.
The most common electronic automotive components are:
- Diodes and transistors: Control power flow in critical systems like engine management and electric vehicle (EV) powertrains.
- Sensors and microcontrollers: Enable advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), including collision detection, lane assist, and parking assistance.
- LEDs and capacitors: Power energy-efficient lighting systems, dashboard displays, and infotainment centers.
3. Healthcare Technology
Circuit components ensure the precision and reliability required in life-saving medical devices and diagnostic equipment.
The most common healthcare technology components are:
- Photodetectors and image sensors: Used in diagnostic tools like X-ray machines, MRI scanners, and medical imaging devices.
- Capacitors and resistors: Regulate power in life-support systems such as ventilators and defibrillators.
- Integrated circuits (ICs): Drive wearable medical devices, enabling remote monitoring of vital signs and real-time data collection.
3. Industrial Automation
In industrial settings, circuit components play a critical role in optimizing processes, reducing downtime, and ensuring operational precision.
The most common industrial automation components are:
- Switches and relays: Control machinery operations in manufacturing plants and automated assembly lines.
- Power supplies and transformers: Provide stable energy to robotics and heavy equipment, providing uninterrupted workflows.
- Sensors and controllers: Enable precision in monitoring temperature, pressure, and motion in industrial systems.

How AGS Devices Supports Various Types of Circuit Components
AGS Devices specializes in the distribution of high-quality types of circuits and circuit components, ensuring each product meets stringent industry standards.
Our comprehensive quality control system guarantees authenticity, and the high-performance standards required in various applications.
We also distribute electronic components, including:
- Power Supply Distributors
- Semiconductors for Sale
- Circuit Protection
- Interconnects
- Passive Components Electronics
- Electronic Testing Equipment
- Electromechanical Devices
We are dedicated to supplying circuit components that are both reliable and durable. The team at AGS understands the critical role these components play in electronic circuits, and we have robust procedures in place to make sure every part we distribute contributes to the optimal functioning of your projects.
As a leading distributor of circuit components, our goal is to boost the efficiency and reliability of your supply chain.